Text Classification in Excel 365
The Text Classification analysis integrates the functionality provided by the Text Classification API, that is, it allows to assign one or more categories to any text according to the model selected. The model used to classify the input text may be either one of the models included in the API or one of the models defined by the user.
For every language there's a default model that follows the International Press Telecommunications Council standard (IPTC) for news, which consists of around 1400 categories.
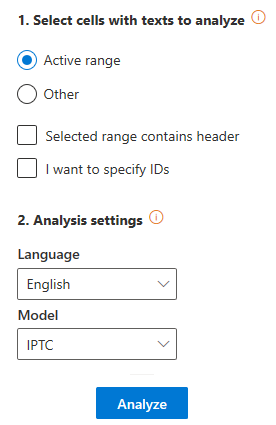
On the right, you can see the interface that appears when you click the Classify text button.
There are two sections in the interface: Select cells with texts to analyze, which we have already covered in the corresponding section, and Analysis settings.
In Analysis settings there are two configurable values to set:
- Language, to select the language of the texts. Refer to the list of supported languages to learn about the languages available.
- Model, to define the model that will be applied to classify the texts. The list of models also includes the user-defined ones associated to the key and language that are being used: they will be identified with a lock icon before the name, as follows:

Advanced settings
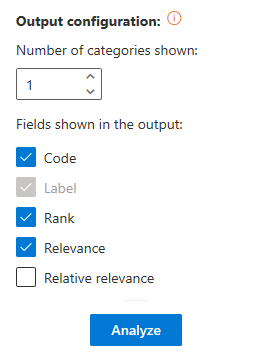
The Advanced settings menu contains additional options for the Text Classification analysis. There is only one section, Output Configuration, to configure the output of the add-in: you can define both the number of categories you want to see in the results and which fields you want to output for each category.
- Number of categories shown: set by default to 1 and with a maximum value of 10.
- Fields:
- Code: shows the code associated to the category.
- Label: shows the label of the category; it's non-configurable, so it always appears in the results.
- Rank: shows the rank or order in which a category has been associated to a text.
- Relevance: shows the absolute relevance associated to the category.
- Relative Relevance: shows the relative relevance associated to the category.
There's more information about each one of these fields in the response section of the API documentation.
Output
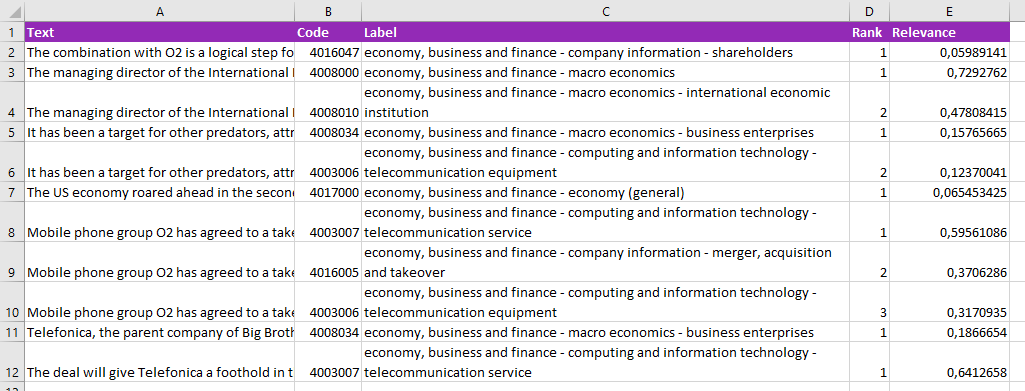
The results obtained from the classification will be shown in a new spreadsheet called "Text Classification". This sheet will include a column with the source text, a column with the IDs if enabled, and a column for each one of the output fields configured in the advanced settings.
When the analysis is configured to output more than one category, each additional category associated to a text will be inserted as a new row, enabling a more flexible use of the results.
This is an example of a possible output of texts in English classified using the IPTC model and without using IDs. The configuration is set to show the default output fields and up to 3 categories: